The Role of GPS Tracker in Risk Control of Automotive Finance
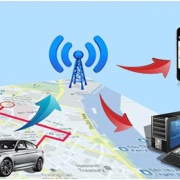
In recent years, the role of GPS trackers in risk control in automotive finance has become increasingly important, as car lenders attempt to reduce risk and ensure timely payment by borrowers. GPS trackers are small devices installed on vehicles, allowing lenders and other stakeholders to track the location and movement of these vehicles in real-time. In this article, we will explore the various uses of GPS trackers in automotive finance and how they can help manage risks and improve overall loan performance.
One of the main benefits of GPS trackers is that they allow lenders to monitor the whereabouts of their financing vehicles at any time. This gives lenders greater visibility into the actions of their borrowers and provides important data that can be used to assess the risk of default. For example, if a borrower frequently travels to high-risk areas or drives abnormally, this may be an indicator that they have a greater risk of defaulting on loans. By monitoring these patterns, lenders can take proactive measures to reduce this risk, such as raising interest rates, requiring additional collateral, and even recovering vehicles.
Another way for GPS trackers to help control automotive financial risks is to provide insights into vehicle use and maintenance. By tracking the mileage and usage patterns of the vehicle, lenders can better understand the overall wear and tear of the vehicle and determine whether the borrower is using it in a responsible and sustainable manner. Similarly, GPS trackers can help ensure that vehicles are properly maintained by monitoring factors such as oil changes, tire rotation, and other routine maintenance tasks. This can help prevent expensive repairs and ensure that borrowers comply with their loan agreements.
In addition to tracking and monitoring the vehicle itself, GPS trackers can also help prevent fraud and ensure compliance with loan terms. For example, lenders can use GPS data to verify whether borrowers use their vehicles for predetermined purposes, such as driving to work or school, rather than engaging in fraudulent activities, such as operating taxi services or using cars for commercial purposes. GPS data can also be used to enforce loan terms related to geographical restrictions, such as prohibiting borrowers from driving their vehicles out of state or within a certain range of their home addresses.
In addition to these specific usage scenarios, GPS trackers can also provide more benefits for lenders and borrowers. By increasing transparency and providing clear records of vehicle activities, GPS data can improve communication and trust between lenders and borrowers. This is particularly important in situations where borrowers have overdue payments or other issues, as it can help rebuild confidence and establish clear expectations for future loan behavior.
Finally, GPS trackers can become a valuable tool to help lenders recover their assets in the event of default. By providing real-time location data of vehicles, lenders can quickly and effectively locate and retrieve the vehicle if necessary. This can ensure that lenders can recover the full value of assets in the event of borrower default, thereby helping to reduce the overall risk of the loan.
In summary, GPS trackers play a crucial role in risk control in automotive finance, providing lenders with valuable data and insights on the location, use, and maintenance of their financing vehicles. By monitoring these factors, lenders can better assess default risks, prevent fraud and violations, improve communication with borrowers, and more effectively recover assets in the event of default. With the continuous development and increasing complexity of the automotive finance industry, GPS trackers may become an increasingly important tool for lenders and other stakeholders.